How to run the project
Running the project
There are 2 ways to run the project:
- The simplest way to run the project is using Docker containers which will run the full-fleged VulnerableApplication with all the components. For running as Docker application, follow following steps:
- Download and Install Docker Compose
- Clone this Github repository
- Open the terminal and Navigate to the Project root directory
- Run the command
docker-compose pull && docker-compose up - Navigate to browser and visit
http://localhostand this will give the User Interface for VulnerableApp.
Note: The above steps will run the latest unreleased VulnerableApp version. If you want to run the latest released version, please use docker latest tag.
- Another way to run the VulnerableApp is as standalone Vulnerable Application is:
- Navigate to Releases Section in github and download the Jar for the latest released version
- Open the terminal and navigate to the project root directory
- Run the command
java -jar VulnerableApp-* - Navigate to browser and visit
http://localhost:9090/VulnerableApp. This will give the Legacy User Interface for the VulnerableApp.
Building the project
There are 2 ways in which this project can be built and used:
- As a Docker application which will help in running the full-fledged VulnerableApplication. For running as Docker application, follow following steps:
- Build the docker image by running
./gradlew jibDockerBuild - Download Docker-Compose and run in the same directory
docker-compose up - Navigate to browser and visit
http://localhostand this will give the User Interface for VulnerableApp.
- Build the docker image by running
- As a SpringBoot application which will run with the Legacy UI or Rest API but gives the benefit of debugging and solving issues. This is the simple way,
- Import the project into your favorite IDE and run it
- Navigate to browser and visit:
http://localhost:9090/VulnerableAppand this will give the Legacy User Interface for VulnerableApp which you can use to debug and test.
Glimpse of ReactJS based User Interface
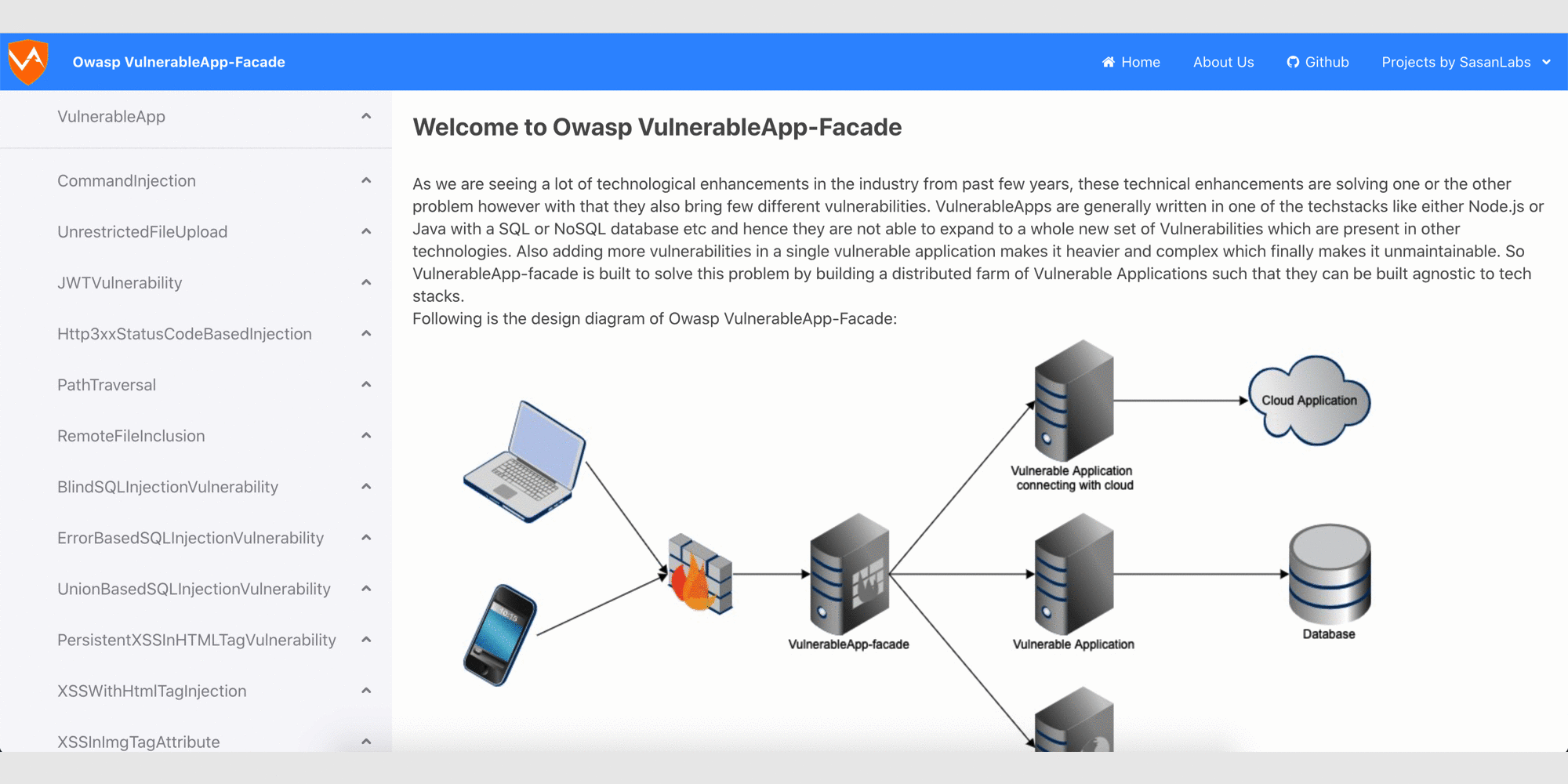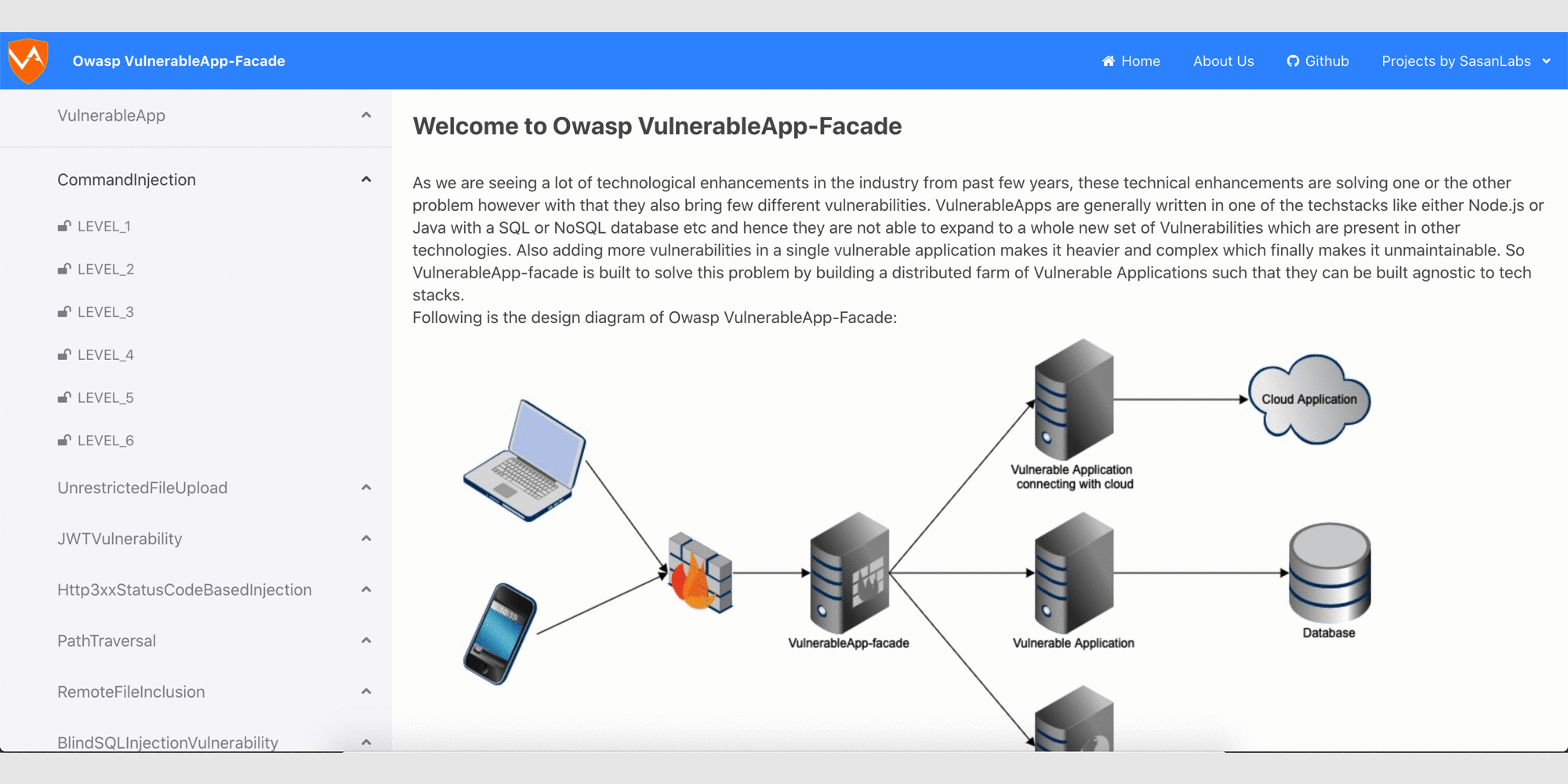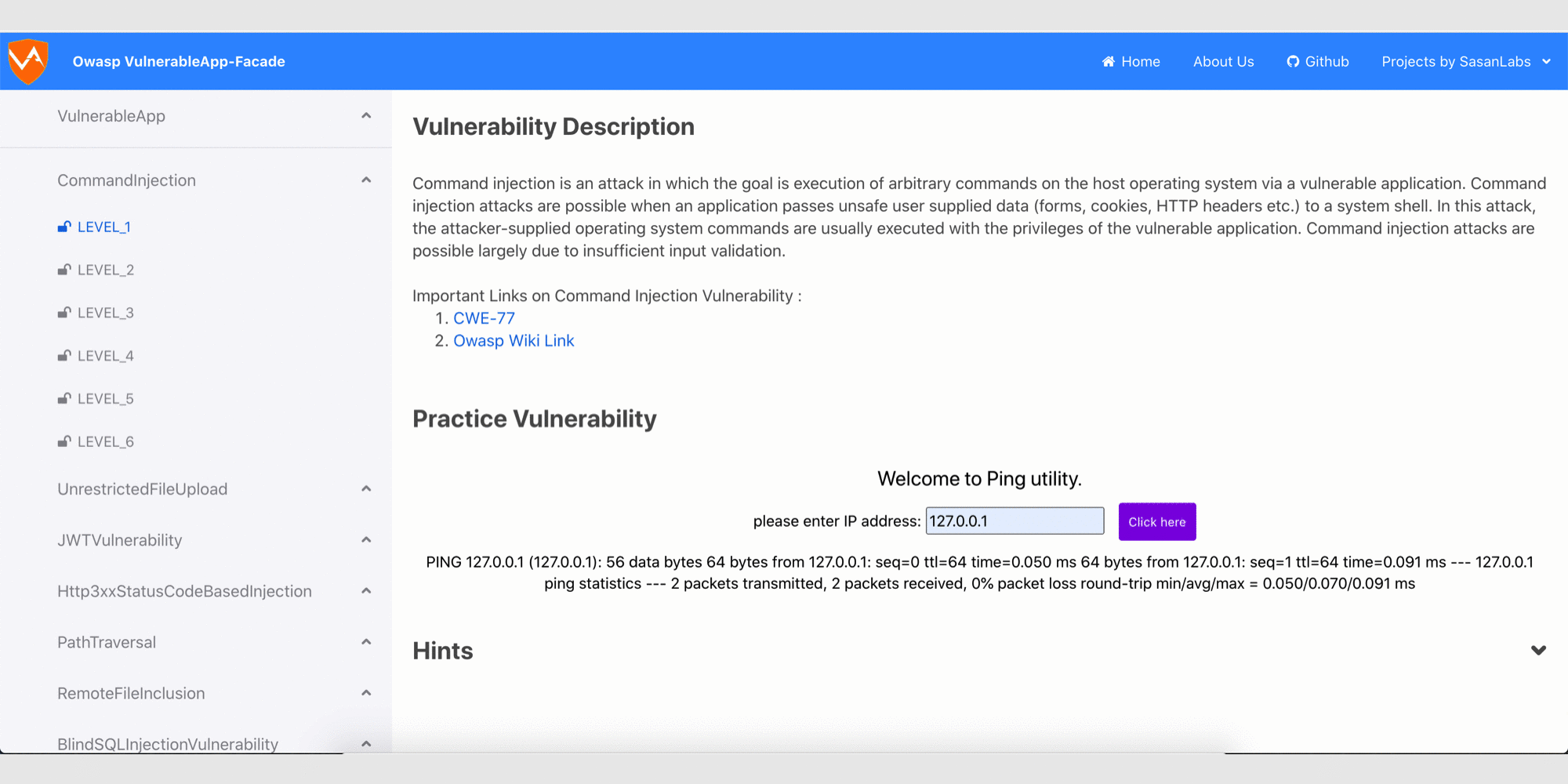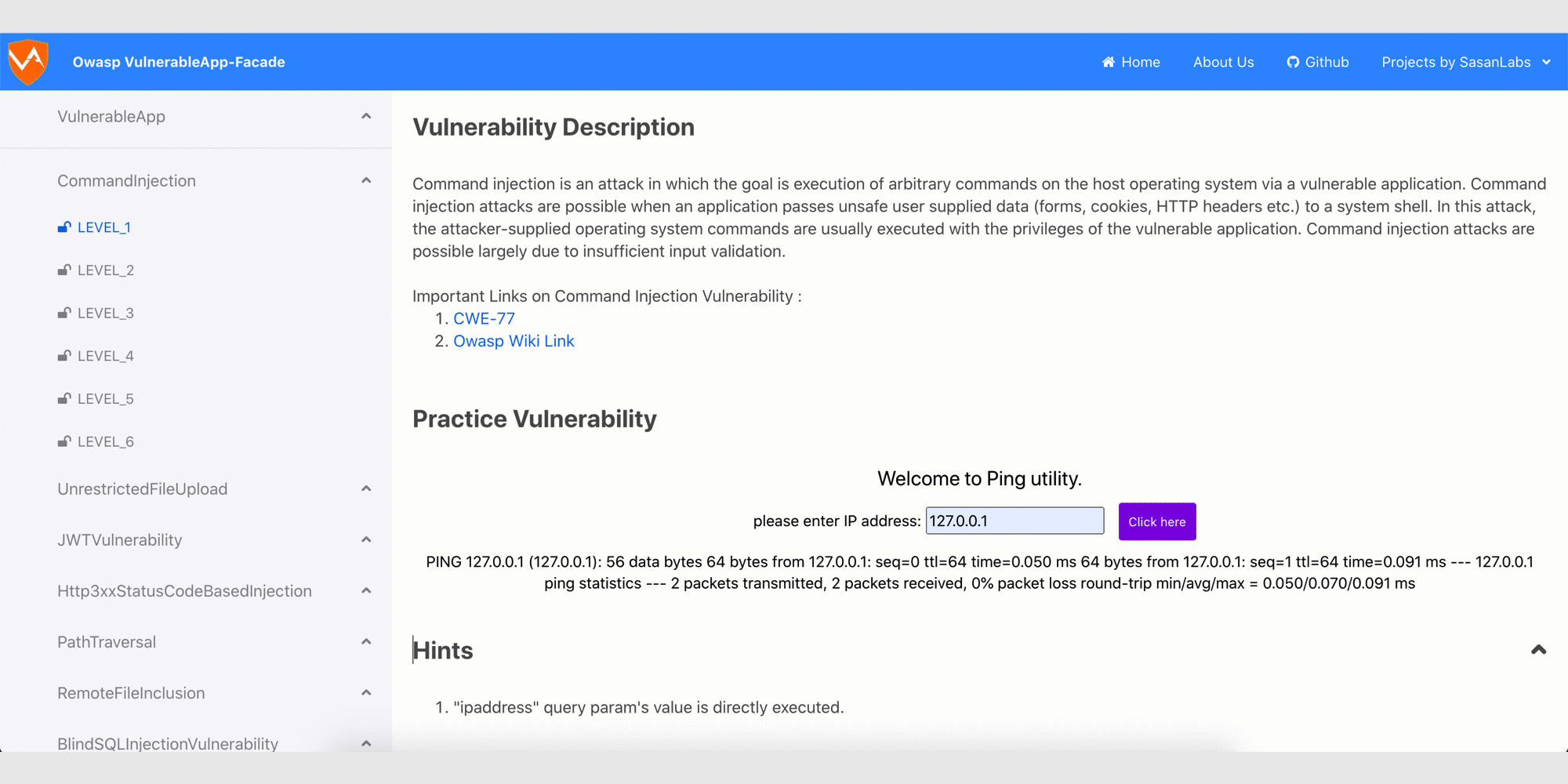
Glimpse of the Legacy User Interface

How SAST or DAST can use the project
As VulnerableApp is built for scanning tools hence there are multiple ways in which they can leverage the VulnerableApp.
- Developer of these scanning tools can add new vulnerabilities for testing there scan rules, payload testing etc. They can even go with TDD approach where they first write the Vulnerable code and then they can write the Scan Rules.
- For Evaluation of scanning tools
- For DAST, VulnerableApp exposes an endpoint
http://<baseurl>/VulnerableApp/scannerwhich provides information about all the Vulnerabilities present in the VulnerableApp which DAST tools can leverage to evaluate themselves. - For SAST, we have added a ExpectedIssues.csv file which has vulnerabilities and their line numbers which SAST tools can use to evaluate themselves.
- For DAST, VulnerableApp exposes an endpoint
Details about scanner endpoint
scanner endpoint exposes following information which DAST tools can leverage:
url: The URL of the endpoint in VulnerableApp.
variant: Whether the endpoint is SECURE or UNSECURE. SECURE is helpful in figuring out the false positives.
method: Type of HTTP method for the endpoint like GET or POST
vulnerabilityTypes: List of vulnerability types present in the endpoint to validate if scanner is fully finding all the vulnerabilities in an endpoint.
Note: VulnerabilityTypes are custom values as no single standard represent all the Vulnerabilities. However we are working on creating a mapping between VulnerabilityType and CWE/WASC.
Details about ExpectedIssues.csv
ExpectedIssues.csv contains following information which SAST tools can leverage:
Vulnerability Type: type of vulnerability present
CWE: CWE id for the Vulnerability
WASC: WASC id for the Vulnerability
File: Full path of the file containing the Vulnerability
Line: Line number in the file containing the Vulnerability
Source: Number of times that line is executed.